A push (reverse pull) test is a method where the principal goal is to apply a downward load onto a sample to measure response as a function of applied downward load. This downward load may be destructive (to part failure) or non-destructive (to force threshold) as needed. For non-destructive tests, force may be applied once or cyclically to evaluate part performance over repeated loading cycles. Most common example of push test: 3-point and 4-point bending and pin test applications.
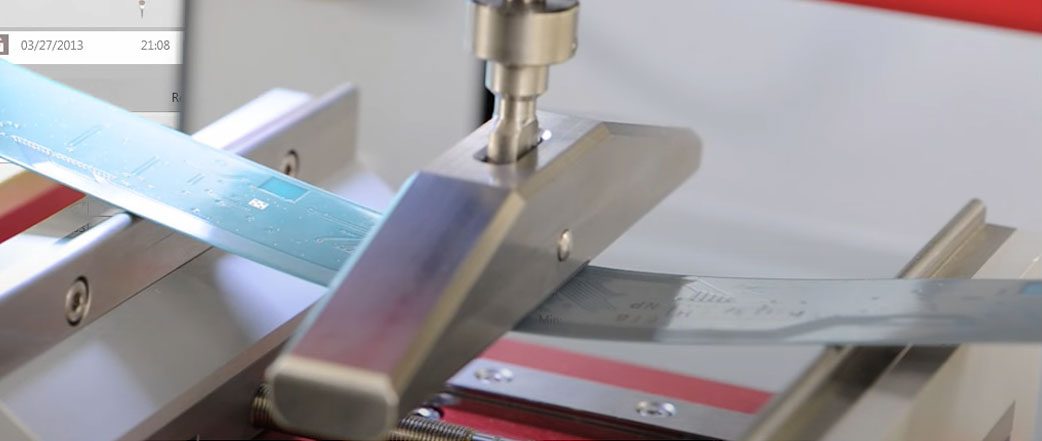


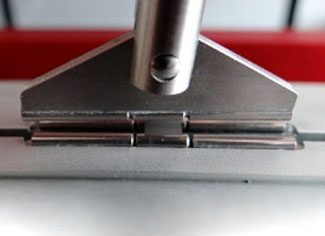

Click the play button to see a push test type video or read more by clicking on the link below.
世界中の支店・代理店がお客様をサポート
オランダ
J.F. Kennedylaan 14b
5981 XC
Panningen
The Netherlands
ドイツ
Am Haupttor / Bürocenter
06237
Leuna
Germany
アメリカ
170 Commerce Way
Suite 200
Portsmouth, NH 03801
United States
72/7 M.12 Soi. Soonthornwipak
Bangpla, Bangphli,
10540 Samut Prakan
Thailand
台湾
No. 157, Zhongzheng
6th St., Hukou
Township, Hsinchu
County 303,
Taiwan (R.O.C.)
蘇州
Room 2012
Haichuang Mansion,
No.288 Dengyun Road,
High-tech district, Kunshan,
Jiang Su, China
該当地区の代理店に問い合わせ
Xyztec develops world-class bond testing technologies and works together with global partners to provide local support worldwide.
J.F. Kennedylaan 14b
5981 XC
Panningen
The Netherlands

Herbert Stuermann